From TinCanTools
This guide will walk you through connecting the Flyswatter3 and the Ubiquiti RouterStation Pro to your Linux PC, and installing and running OpenOCD. This guide was written with Ubuntu 10.04.
Contents
- 1 Connecting the Flyswatter3 and the RouterStation Pro
- 1.1 Connect the JTAG ribbon cable to the Flyswatter3.
- 1.2 Connect the Other End of the Ribbon Cable to the RouterStation Pro.
- 1.3 Connect the RS-232 Serial Cable.
- 1.4 Connect the USB Cable to the Flyswatter3.
- 1.5 Connect the CAT6 Cable to the Power Over Ethernet Injector.
- 1.6 Connect the Power Adapter to the Power Over Ethernet Injector.
- 1.7 Connect the Other End of the CAT6 Cable to the RouterStation Pro.
- 1.8 Plug the Power Adapter into a Wall Outlet.
- 1.9 Plug the USB Cable into your PC.
- 2 Installing OpenOCD
- 3 Running OpenOCD
- 4 Common OpenOCD Commands
- 5 GDB Debugger
Connecting the Flyswatter3 and the RouterStation Pro
To hook up the Flyswatter3 and the RouterStation Pro, you will need:
- Flyswatter3
- USB Male A/Male B Cable
- 14-pin JTAG Ribbon Cable
- RouterStationPro
- RS-232 Serial Cable with two female connectors
- CAT6 Cable
- Power Over Ethernet Injector (with power cable)
The items listed under Flyswatter3 ship with the Flyswatter3. The items listed under RouterStationPro are included with the MIPS Linux Starter Kit.
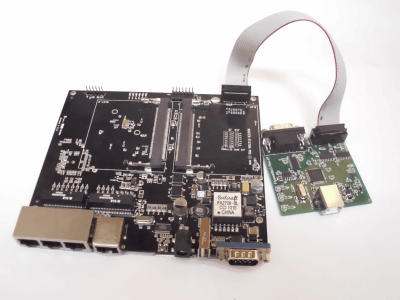
Connect the JTAG ribbon cable to the Flyswatter3.
The ribbon cable should have a notch on the connector to force it into the correct position. If it doesn't, make sure to align Pin 1 of the adapter as shown in the image to the left. (Pin 1 is on the side of the cable with the red stripe.)
Connect the Other End of the Ribbon Cable to the RouterStation Pro.
Again, be sure to align the red stripe with Pin 1, as shown in the picture. Pin 1 is toward the outer edge of the board. It is also marked on the bottom of the RouterStation Pro.
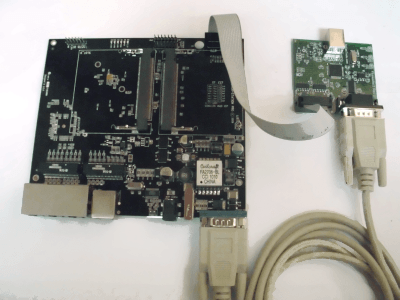
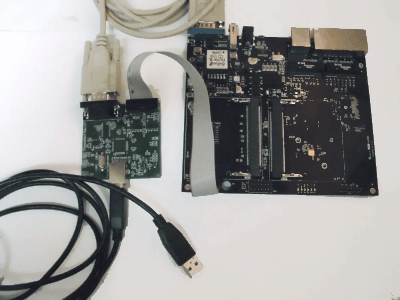
Connect the RS-232 Serial Cable.
Connect the cable as shown in the picture.
Connect the USB Cable to the Flyswatter3.
Connect the Male B adapter to the Flyswatter3. (The Male B end is the squarish end, not the flat end.)
Connect the CAT6 Cable to the Power Over Ethernet Injector.
Leave the boards alone for now. Find the Power Over Ethernet Injector in the MIPS Linux Starter Kit, and connect the CAT6 cable. The PoE injector has two ethernet ports, but only one supplies power. Be sure to use the correct one. The correct ethernet port is labeled.
Connect the Power Adapter to the Power Over Ethernet Injector.
Connect the power cable to the other side of the PoE injector.
Connect the Other End of the CAT6 Cable to the RouterStation Pro.
Connect the CAT6 cable to the RouterStation Pro's Power Over Ethernet port. Warning: The RouterStation Pro has three ethernet ports in addition to the PoE port. Connecting the PoE injector to one of the regular ethernet ports may damage the board. The PoE port is the closest to the center of the board, to the right of the three ethernet ports as shown in the picture. It is labeled POE on the board.
Plug the Power Adapter into a Wall Outlet.
The green LEDs on the RouterStation Pro should briefly flash, and the leftmost LED should remain on.
Plug the USB Cable into your PC.
The green power LED on the Flyswatter3 should come on and remain on.
Installing OpenOCD
OpenOCD (Open On-Chip Debugger) is open-source software that interfaces with the Flyswatter3. OpenOCD provides debugging and in-system programming for embedded target devices. You will need to compile OpenOCD from source, and patch the source with one of the OpenOCD Patches for Flyswatter 3 support.
Whichever guide you use, be sure to install the patch! Both guides include instructions on downloading and installing the patch.
The first set of instructions uses libFTDI, an open-source driver library for FTDI devices. The second set uses FTD2XX, a closed-source driver library from Future Technology Devices International.
Running OpenOCD
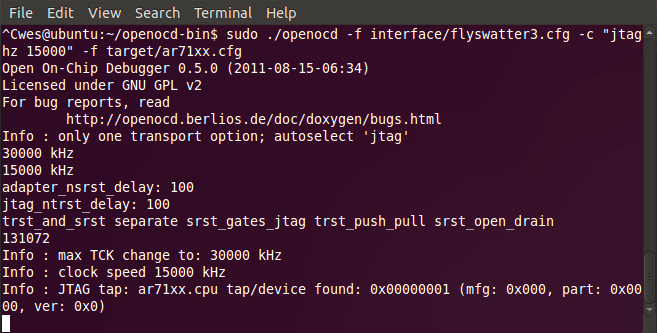
Now you are ready to run OpenOCD. If you installed the OpenOCD Ubuntu package, open a terminal window and type the following from any directory:
openocd -f interface/flyswatter3.cfg -c "jtag_khz 15000" -f target/ar71xx.cfg
If you compiled OpenOCD yourself, navigate to the openocd-bin directory you created in the compile guide and type:
cd ~/openocd-bin sudo ./openocd -f interface/flyswatter3.cfg -c "jtag_khz 15000" -f target/ar71xx.cfg
Your terminal window should now look something like this:
Telnet Connection
You cannot enter commands directly to OpenOCD. Open a new terminal window and type:
telnet localhost 4444
You will should see this prompt:
You can give commands to OpenOCD through this prompt.
Common OpenOCD Commands
To see a full list of OpenOCD commands, enter help in the telnet window.
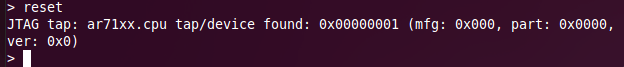
reset
Resets the RouterStation Pro. The output of the Reset command should look like this:
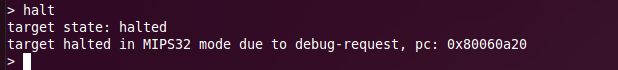
halt
Sends a halt request to the RouterStation Pro. If the RouterStation Pro halts, you will see text output in the telnet window. (If the RouterStation Pro is already halted, you will see no output.)
halt [timeout]
You can also use halt followed by a time in milliseconds. OpenOCD waits for the target to halt the specified amount of time, then gives up if the target has not halted. You can use this to avoid OpenOCD hanging because the RouterStation Pro fails to halt. For example, to send a halt command with a timeout of one second, type:
halt 1000
resume
Enter resume to end a halt. You will not see any text output in the telnet window.
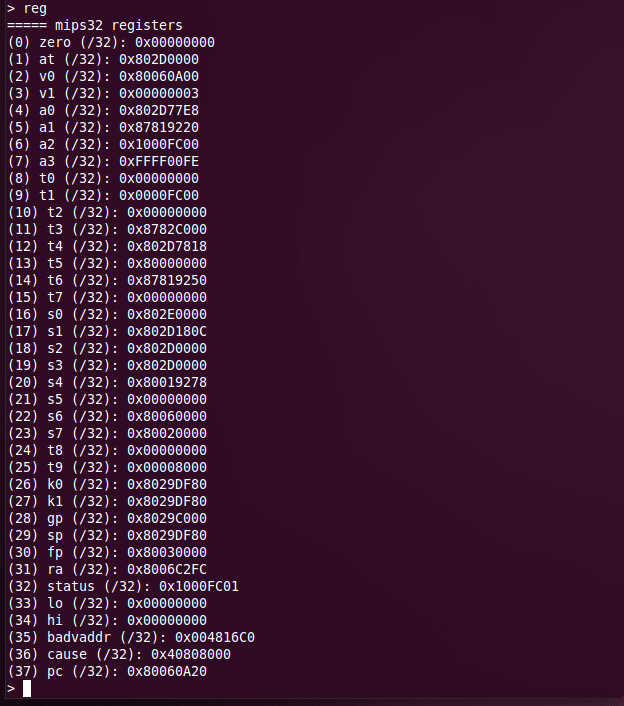
reg
Displays a numbered list of all of the RouterStation Pro's registers.
If the board is not halted, the list of registers will be displayed but not their values.
reg [entry]
Run reg with a register number to display the contents of a register, in hexadecimal. The register number corresponds to the output of the reg command with no arguments, above. You must run the halt command before reading registers.
If you run reg while the RouterStation Pro is not halted, you will still see the value stored in the register. However, registers change contents very quickly while the device is running; by the time you see the value, the value actually in the register may be different. If you try to run reg while the device is not halted, you will see this:
Note that the RouterStation Pro does not show any warning if you run the reg command while the board is running.
reg [entry] [value]
Sets the value of a register. The register number corresponds to the output of the reg command with no arguments, above. Make sure the RouterStation Pro is halted (with the halt command) before you change the value of a register!
You can enter registry values in either decimal, by typing a number by itself, or in hexadecimal, by prefacing the value with 0x.
GDB Debugger
GDB, the GNU Project Debugger is a debugging tool provided with the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC). GDB allows you to stop and start a running program, examine its functioning, and make changes. GDB is installed on Ubuntu 10.04 by default, but you will need a different version of GDB build for embedded targets. Follow the instructions on the GDB Debugger page below.
The GDB debugger page will walk you through installing GDB for use with OpenOCD, and loading and testing a simple program.